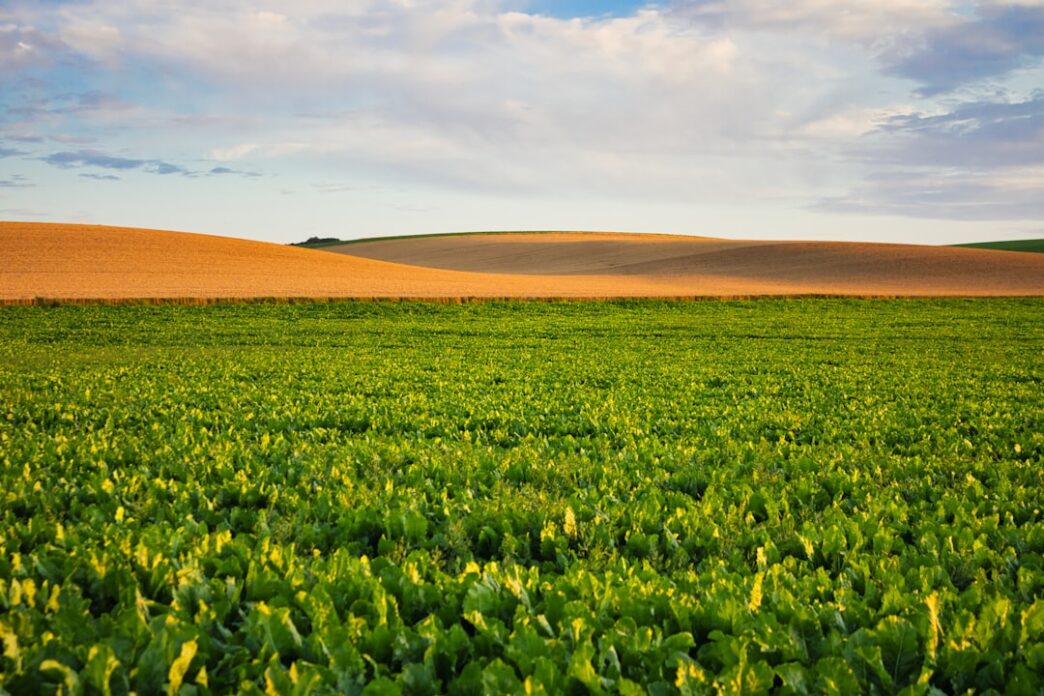
Amid growing concerns over climate change and food security, regenerative agriculture is garnering attention as a promising solution to enhance agricultural productivity while restoring ecological balance. Unlike conventional farming practices that often deplete soil nutrients and rely heavily on chemical inputs, regenerative agriculture emphasizes holistic management, aiming to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon.
Farmers and agronomists around the world, from the heartland of the United States to the plains of Brazil, are adopting practices that prioritize soil regeneration, such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and agroforestry. These methods not only enhance soil fertility but also mitigate the adverse effects of climate change by drawing down carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
One striking example is the work of the Rodale Institute in Pennsylvania, which has been at the forefront of regenerative agriculture research. The institute’s long-term studies demonstrate that regenerative practices can yield as much, if not more, than conventional methods while substantially improving soil health. This evidence is crucial for gaining traction among traditional farmers who may be hesitant to abandon time-tested practices.
However, the transition to regenerative agriculture is not without its challenges. Farmers often face significant initial costs, uncertainty about yield outcomes, and a lack of access to markets that support sustainably produced goods. Organizations like the European Union have initiated programs aimed at incentivizing regenerative practices through subsidies and grants. The EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy aims to make food systems fair, healthy, and environmentally-friendly, encouraging farmers to embrace these transformative practices.
The economic implications of regenerative agriculture extend beyond individual farms. As resilience becomes a priority in agricultural policy, nations that invest in sustainable practices can potentially enhance food security and support rural economies. For instance, in countries like Kenya, where climate variability poses a threat to subsistence farming, adopting regenerative practices could mean the difference between survival and economic collapse. Local farmers adopting agroecological methods have reported improved crop yields and resilience to climate shocks, illustrating a viable path to sustainable livelihoods.
Yet, the narrative surrounding regenerative agriculture is complicated by economic inequities. Large agribusinesses, which dominate the agricultural sector, may monopolize markets, limiting opportunities for smallholder farmers who wish to transition to these practices. Addressing these disparities is essential to ensure that the benefits of regenerative agriculture are equitably distributed.
While regenerative farming is gaining momentum, it requires coordinated efforts from governments, NGOs, and the private sector to create enabling environments for farmers. Consumer demand for sustainably produced food is rising, and this could further incentivize the shift. The rise of food cooperatives and direct-to-consumer models enables farmers to capture more value from their products, promoting a more equitable food system.
As regenerative agriculture continues to evolve, it represents a beacon of hope for not only improving agricultural productivity but also fostering economic resilience and addressing climate change. The dialogue around this revolutionary farming practice is only beginning, and it might just redefine our approach to food production for generations to come. As stakeholders across sectors recognize the interconnectedness of ecology and economy, the real work of building a sustainable future can begin.